WHO said the virus is endemic in some animal populations in a number of countries, leading to occasional outbreaks among local people and travelers, reports Asian Lite News
The World Health Organization (WHO) has confirmed 80 cases of monkeypox in 11 countries and said they are working to better understand the extent and cause of the outbreak.
In a statement issued on Friday, the WHO said the virus is endemic in some animal populations in a number of countries, leading to occasional outbreaks among local people and travelers.
“WHO and partners are working to better understand the extent and cause of an outbreak of monkeypox. The virus is endemic in some animal populations in a number of countries, leading to occasional outbreaks among local people and travelers. The recent outbreaks reported across 11 countries so far are atypical, as they are occurring in non-endemic countries,” the WHO said in a statement.
“There are about 80 confirmed cases so far, and 50 pending investigations. More cases are likely to be reported as surveillance expands,” it added.
The world health organization said it continues to receive updates on the status of ongoing outbreaks in endemic countries to expand disease surveillance.
“Monkeypox spreads differently from COVID-19. WHO encourages people to stay informed from reliable sources, such as national health authorities, on the extent of the outbreak in their community (if any), symptoms and prevention,” the statement added.
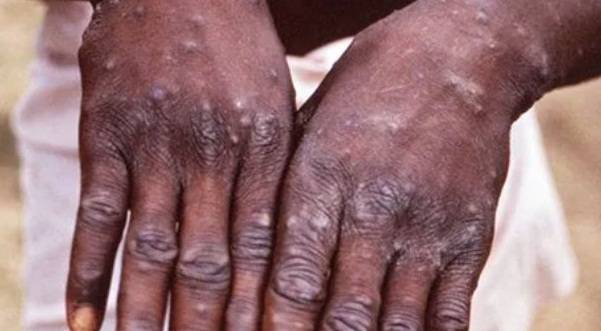
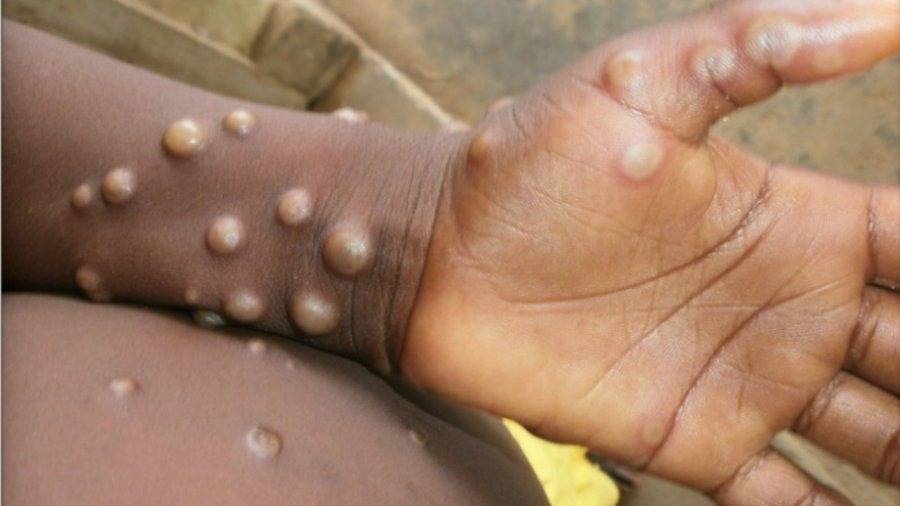
Monkeypox is a viral zoonosis (a virus transmitted to humans from animals) with symptoms very similar to those seen in the past in smallpox patients, although it is clinically less severe.
According to WHO, Monkeypox typically presents clinically with fever, rash and swollen lymph nodes and may lead to a range of medical complications. Monkeypox is usually a self-limited disease with symptoms lasting from 2 to 4 weeks.
Issuing an alert to the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) and Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), the Central government has asked them to keep a close watch on the monkeypox situation and send samples of symptomatic travellers to the National Institute of Virology (NIV) in Pune for further investigation.
“Keep a close watch on monkeypox situation abroad. Send samples (to NIV, Pune) only in such cases where people display certain specific symptoms. Not samples of sick passengers,” sources told ANI. (ANI)