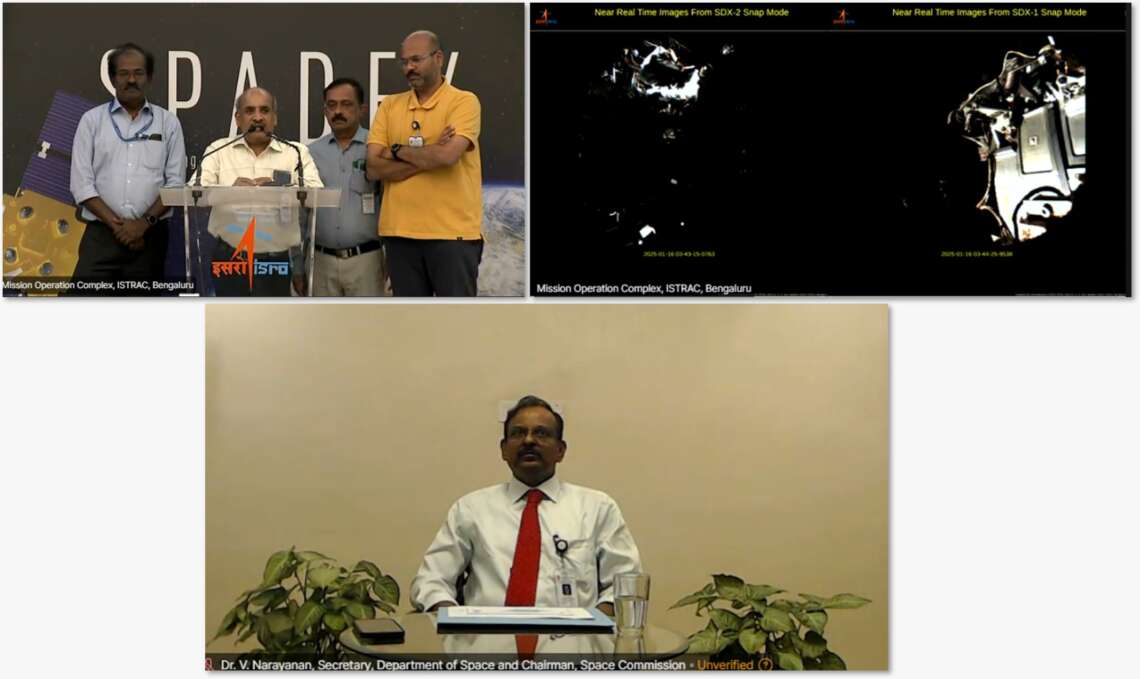
The mission, originally scheduled for Wednesday, was postponed due to an anomaly detected in the PROBA-3 spacecraft. ..reports Asian Lite News
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched the PSLV-C59/PROBA-3 mission from Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, on Thursday.
The PSLV-C59 vehicle is carrying the Proba-3 spacecraft into a highly elliptical orbit as part of a dedicated commercial mission by NewSpace India Limited (NSIL).
The mission, originally scheduled for Wednesday, was postponed due to an anomaly detected in the PROBA-3 spacecraft.
The PSLV-C59 mission is a joint initiative between ISRO and NewSpace India Limited (NSIL).
Proba-3 is a technology demonstration mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) and marks ESA’s first precision formation-flying mission. It involves a pair of satellites flying together in a fixed configuration, as if forming a single large rigid structure in space, to showcase innovative formation-flying and rendezvous technologies.
According to ESA, the mission will demonstrate formation flying within the context of a large-scale scientific experiment. The two satellites will create an approximately 150-metre-long solar coronagraph to study the Sun’s faint corona closer to the solar rim than has ever been achieved before.
In addition to its scientific goals, the mission serves as a benchmark for achieving precise positioning between two spacecraft, employing a wide range of new technologies.
Proba-3 will function as an orbital laboratory, demonstrating acquisition, rendezvous, proximity operations, and formation flying while validating advanced metrology sensors and control algorithms. This mission aims to pave the way for innovative approaches to mission control. The two satellites will maintain a fixed 150-metre configuration in space, aligned with the Sun, enabling the Occulter Spacecraft (OSC) to block the solar disk for the Coronagraph Spacecraft (CSC). This alignment will provide uninterrupted views of the Sun’s faint corona for scientific study.
The Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is India’s first launch vehicle to feature liquid stages and is employed to carry satellites and other payloads into space based on ISRO’s requirements. The PSLV’s first successful launch took place in October 1994.
According to ISRO, PSLV-C59 involves four stages and carries a total payload mass of approximately 320 tonnes.
The ISRO said that the mission reflected the dedication of NewSpace India Limited (NSIL), ISRO and European Space Agency (ESA) teams. This achievement highlights India’s critical role in enabling global space innovation, ISRO added.
ISRO successfully launched the PSLV-C59/PROBA-3 mission from Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh earlier today.
The PSLV-C59 vehicle is carrying the Proba-3 spacecraft into a highly elliptical orbit as part of a dedicated commercial mission by NewSpace India Limited (NSIL).
The mission, originally scheduled for Wednesday, was postponed due to an anomaly detected in the PROBA-3 spacecraft.
The PSLV-C59 mission is a joint initiative between ISRO and NewSpace India Limited (NSIL).
Proba-3 is a technology demonstration mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) and marks ESA’s first precision formation-flying mission. It involves a pair of satellites flying together in a fixed configuration, as if forming a single large rigid structure in space, to showcase innovative formation-flying and rendezvous technologies.
According to ESA, the mission will demonstrate formation flying within the context of a large-scale scientific experiment. The two satellites will create an approximately 150-metre-long solar coronagraph to study the Sun’s faint corona closer to the solar rim than has ever been achieved before.
In addition to its scientific goals, the mission serves as a benchmark for achieving precise positioning between two spacecraft, employing a wide range of new technologies.
Proba-3 will function as an orbital laboratory, demonstrating acquisition, rendezvous, proximity operations, and formation flying while validating advanced metrology sensors and control algorithms. This mission aims to pave the way for innovative approaches to mission control.
The two satellites will maintain a fixed 150-metre configuration in space, aligned with the Sun, enabling the Occulter Spacecraft (OSC) to block the solar disk for the Coronagraph Spacecraft (CSC). This alignment will provide uninterrupted views of the Sun’s faint corona for scientific study.
ALSO READ: India, the Forgotten Epicentre of Knowledge and Trade: Dalrymple