This lingering inflammation was significantly associated with elevated body mass index (BMI), metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), higher baseline systemic inflammation, and increased adipose (fat) tissue levels
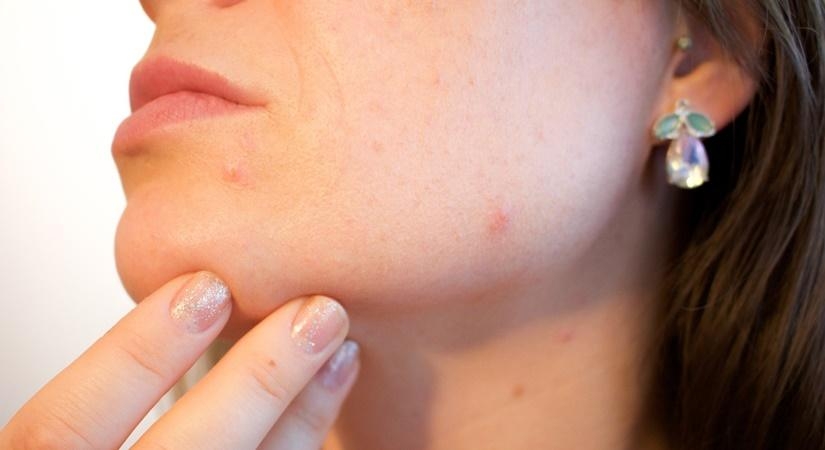
A new international study has revealed that patients with psoriasis—a chronic inflammatory skin condition—may remain at risk of systemic inflammation even after successful skin treatment, increasing their vulnerability to obesity, fatty liver disease, and cardiovascular issues.
Published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, the study sheds light on why treating only the visible symptoms of psoriasis may not be enough. It highlights the lingering presence of inflammation in the body, despite the use of advanced biologic therapies that effectively clear skin lesions.
“Despite excellent control of skin disease, a substantial percentage of psoriasis patients demonstrate residual systemic inflammation,” said Dr. Joel M. Gelfand of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. “These findings emphasise that just treating the skin signs of psoriatic disease is not sufficient, and patients often need additional approaches to lowering systemic inflammation.”
Researchers evaluated 209 psoriasis patients from cohorts in Spain, the US, and Sweden. All patients had achieved no or only mild skin symptoms through stable biologic treatment. However, the study found that 36.3% of these individuals continued to exhibit signs of residual inflammation.
This lingering inflammation was significantly associated with elevated body mass index (BMI), metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), higher baseline systemic inflammation, and increased adipose (fat) tissue levels.
Lead investigator Dr. Álvaro González-Cantero, from the Department of Dermatology at Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal in Spain, emphasized the broader implications. “The findings underscore a critical unmet need to address the systemic inflammatory burden beyond skin symptoms in psoriasis, potentially requiring interventions targeting obesity and metabolic dysfunction to improve overall patient outcomes,” he said.

The researchers propose more comprehensive cardiovascular risk assessments and regular monitoring of inflammatory and liver health markers, such as high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. They also advocate integrating lifestyle changes and weight management strategies into the standard care for psoriasis patients.
While biologics have transformed skin treatment in psoriatic disease, the study urges clinicians to look beyond surface-level symptoms and consider the deeper, systemic risks that may persist. The team called for further studies to validate their findings and explore targeted interventions aimed at reducing inflammation at the systemic level.
The results of this study could reshape the approach to psoriasis treatment, highlighting the need for a holistic strategy that includes not only dermatological care but also metabolic and cardiovascular risk management.